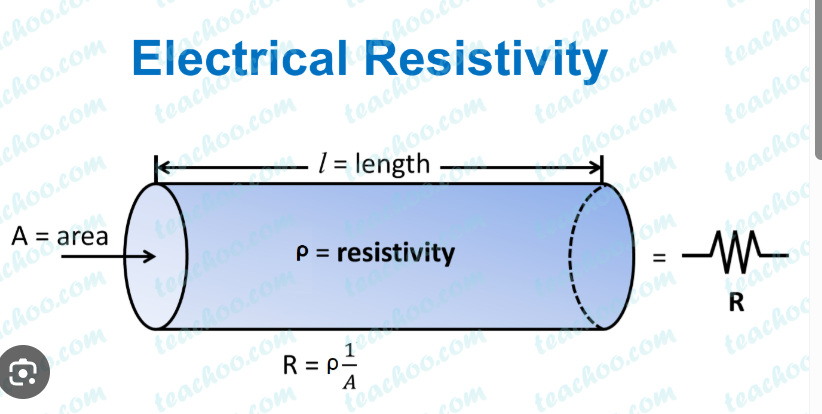
The electrical resistance of a conductor is a measure of how much it opposes the flow of electric current. It depends on several factors, including:
Material – Different materials have different resistivities (e.g., copper has low resistance, while rubber has high resistance).
Length – Longer conductors have higher resistance.
Cross-sectional area – Thicker conductors have lower resistance.
Temperature – Most conductors have higher resistance at higher temperatures.
Formula for Resistance
The resistance of a conductor is given by Ohm’s Law and the resistance equation:
where:
= resistance (ohms, Ω)
= resistivity of the material (Ω·m)
= length of the conductor (m)
= cross-sectional area of the conductor (m²)
Would you like help calculating resistance for a specific conductor? 😊
